Properly storing vegetables is essential to ensure they stay fresh and nutritious for as long as possible. Traditionally, root cellars were the go-to solution for vegetable storage, offering a cool, dark environment ideal for preservation. However, not everyone has access to a root cellar. Fortunately, there are many creative and effective ways to store vegetables without one. Here are some ingenious tips to help you keep your vegetables fresh and flavorful.
Cool and Dark Storage
A cool, dark place is perfect for storing many types of vegetables because it mimics the conditions of a root cellar. Look for spaces in your home that stay relatively cool and dark, such as basements, closets, or even under the stairs. These areas help slow down the ripening process and prevent vegetables from spoiling quickly.
Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial to prevent mold and spoilage. Vegetables need air circulation to stay fresh. Using mesh bags or perforated boxes can help maintain airflow around your produce. Avoid plastic bags that trap moisture, as this can lead to rotting.
Use of Natural Preservatives
Natural preservatives like sand, sawdust, and leaves can help extend the life of your vegetables. For instance, root vegetables like carrots and beets can be stored in a box filled with sand to keep them from drying out. Sawdust and leaves can provide similar benefits, helping to maintain moisture levels and protect vegetables from decay.
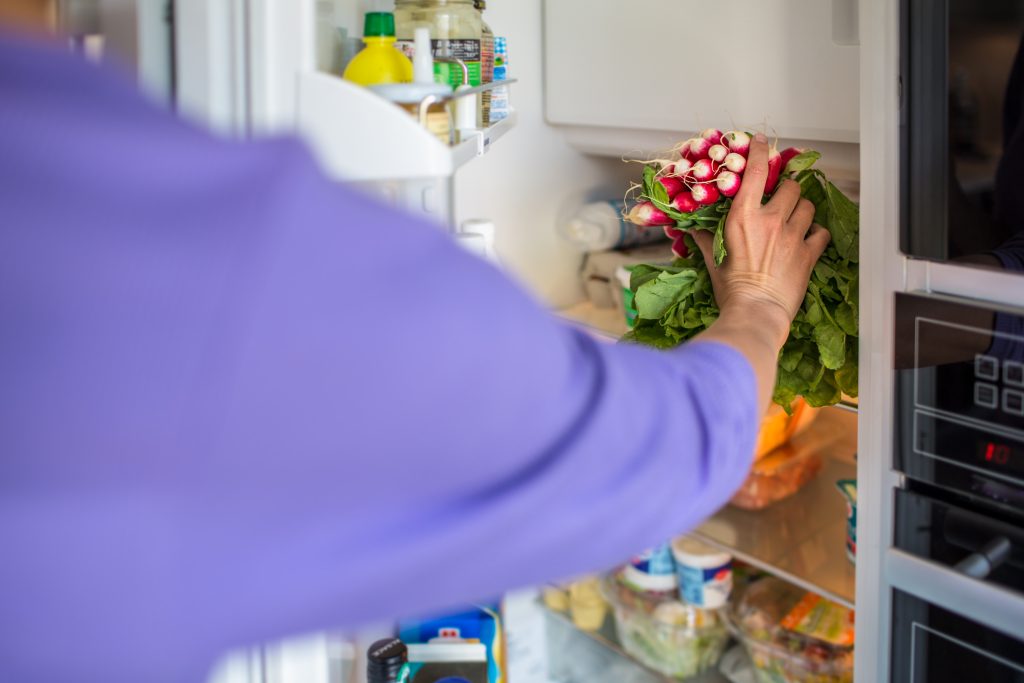

Storing in the Fridge
Certain vegetables can be stored in the fridge to keep them fresh. Leafy greens, carrots, and bell peppers do well in the refrigerator. To maximize storage space and maintain the right humidity levels, use produce drawers and keep vegetables in loosely tied plastic bags or reusable produce bags. This helps retain moisture without causing condensation, which can lead to spoilage.
Curing Root Vegetables
Curing is an essential step for root vegetables like potatoes and onions before long-term storage. The curing process involves drying the vegetables to toughen their skins and improve their storage life. Place freshly harvested root vegetables in a warm, dry place with good ventilation for about two weeks. After curing, they can be stored in a cool, dark place.
Utilizing Freezing Methods
Freezing is a great way to preserve many types of vegetables. Before freezing, blanch vegetables by boiling them briefly and then plunging them into ice water. This process helps preserve color, flavor, and texture. Once blanched, dry the vegetables thoroughly and pack them in airtight containers or freezer bags.
Using Fermentation
Fermenting vegetables is an ancient preservation method that can add a probiotic boost to your diet. Common vegetables for fermentation include cabbage (for sauerkraut) and carrots. To ferment, submerge the vegetables in a saltwater brine and let them sit at room temperature for a few weeks. The natural fermentation process preserves the vegetables and adds beneficial bacteria.
Drying and Dehydration
Drying and dehydrating vegetables is another effective storage method. Dried vegetables are lightweight and take up less space. You can use an oven set to a low temperature or a dedicated food dehydrator to dry vegetables. Once dried, store them in airtight containers to keep moisture out.
There are many ways to store vegetables without a root cellar, each with its own advantages. By using cool and dark storage spaces, ensuring proper ventilation, and experimenting with natural preservatives, refrigeration, curing, freezing, fermentation, and dehydration, you can keep your vegetables fresh and nutritious for longer periods. Try out these methods and find the ones that work best for your available space and resources.