Cow milk, goat milk, and sheep milk each have unique properties that appeal to different health needs and preferences. Understanding the differences can help you make an informed choice about which milk is best for you. With the increasing variety of milk available in the market, it’s essential to know what each type offers in terms of nutrition, digestibility, environmental impact, and more.
Nutritional Comparison
Each type of milk offers a distinct nutritional profile. Cow milk is well-known for being rich in calcium and vitamin D, essential for bone health and overall well-being. It also contains significant amounts of B vitamins and phosphorus. Goat milk, on the other hand, contains higher amounts of vitamin A and potassium, contributing to better skin health and muscle function. Sheep milk stands out with its high levels of protein and beneficial fats, along with impressive amounts of zinc and vitamin B12, supporting immune function and energy production.
Digestibility and Allergies
Many people find goat milk easier to digest than cow milk due to its smaller fat globules and lower lactose content. This makes goat milk a suitable option for those with mild lactose intolerance. Sheep milk, while also easier on the stomach for some, is richer and might be harder to digest for others due to its higher fat content. Additionally, cow milk is more likely to cause allergies, especially in children, because of its protein structure. Goat and sheep milk proteins are less allergenic, making them better alternatives for those with milk allergies.
Fat and Protein Content
Sheep milk has the highest fat and protein content among the three, making it an excellent choice for those needing more calories or muscle support. The fat in sheep milk is mostly unsaturated, which is beneficial for heart health. Goat milk offers a moderate amount of both fat and protein, with fats that are easier to digest and proteins that are less likely to cause inflammation. Cow milk provides a balance of fat and protein that fits well into most diets, but it is often perceived as heavier and more difficult to digest compared to the other two.
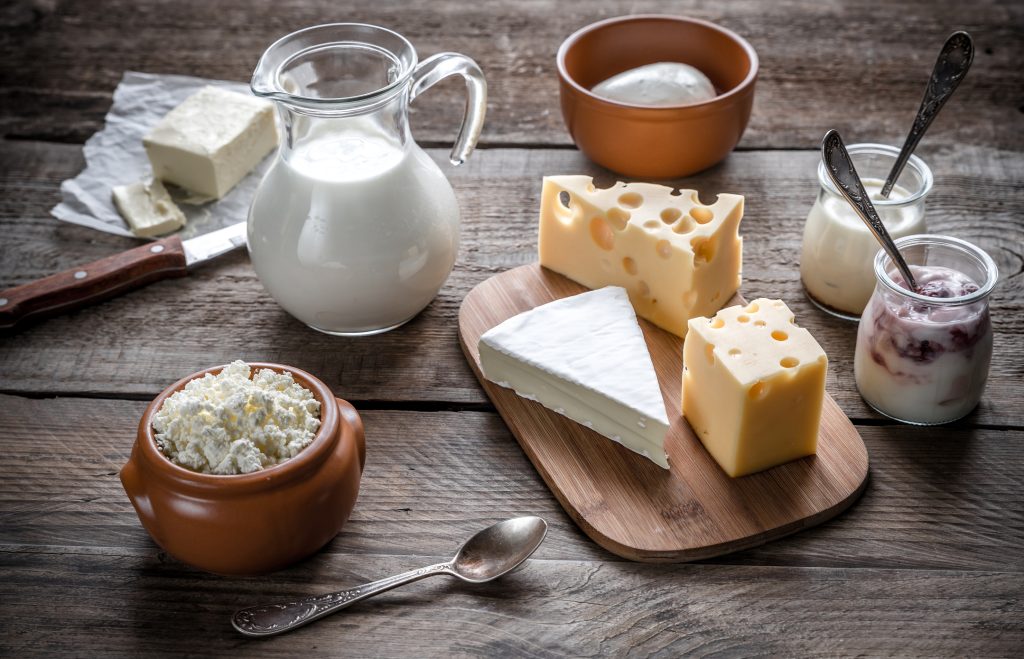

Taste and Culinary Uses
The taste of these milks can vary significantly, influencing their culinary uses. Cow milk is mild and versatile, suitable for drinking, cooking, and baking. Goat milk has a distinct tanginess that some people love and others dislike; it’s particularly popular in cheese-making and yogurt due to its creamy texture. Sheep milk is rich and creamy with a slightly sweet taste, making it ideal for gourmet cheeses and specialty dairy products. Each type of milk brings unique flavors and textures to dishes, from savory to sweet.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of milk production varies. Goat and sheep farming typically require less land and produce fewer greenhouse gases compared to cow farming, making them more sustainable choices. Cows require more feed, water, and space, contributing to higher methane emissions and environmental degradation. In contrast, goats and sheep are more efficient in converting feed into milk and can thrive on less arable land, making their farming practices more environmentally friendly.
Health Benefits and Drawbacks
Cow milk supports bone health with its calcium content, but it can cause allergies and digestive issues in some people. Goat milk is known for its anti-inflammatory properties and easier digestibility, but its strong flavor can be off-putting. Sheep milk is packed with essential nutrients and offers high protein and fat content, but it is more expensive and less available. Each type of milk has specific health benefits: cow milk for bone health, goat milk for digestion and inflammation, and sheep milk for nutrient density.
All three types of milk have their pros and cons. The healthiest choice depends on your individual health needs, dietary preferences, and environmental considerations. Cow milk is widely accessible and nutritionally balanced but may cause allergies. Goat milk is easier to digest and has anti-inflammatory benefits but has a strong flavor. Sheep milk is nutrient-dense and environmentally friendly but is costlier and less common. By weighing these factors, you can choose the milk that best suits your lifestyle and health goals.